Several arrhythmia medications are available. These drugs help to regulate heart rhythm and are prescribed by a physician. Most of these drugs are available in oral form. In some cases, a patient must take an additional medication in addition to the usual prescription medication. There are several possible side effects of arrhythmia medications. Some of these side effects may include dry or flushed skin, headache, constipation, and agitation. Despite the risks, the majority of patients tolerate these medicines well and avoid the complications that come with long-term treatment.
Many different types of medications are available. The most common are beta blockers. These medicines work by slowing the heart cell’s activity. They are more effective for automaticity arrhythmias. Calcium channel blockers reduce the sensitivity of heart muscle cells to electrical signals. Other medications may be used depending on the cause of the arrhythmia. Ask your healthcare provider for a recommendation based on the risks and benefits.
Prescription medications can help treat arrhythmias by changing the electrical pathways. This is especially useful for uncomplicated forms of heart rhythm disturbances. Typically, the goal of antiarrhythmic drugs is to reduce the heart rate to an average of 110 beats per minute. While some patients may experience improvement when their heart rate is adequately controlled, others may continue to suffer from symptoms. However, you should not expect miracles from these drugs.
If you experience any of these side effects, it is important to talk to your doctor about treatment options. Many patients need to be hospitalized before they can start taking antiarrhythmic drugs. Ohio State’s Arrhythmia Unit is located on the seventh floor of Ross Heart Hospital. Here, doctors and pharmacists have developed special protocols for the use of these types of medications. They constantly monitor your heart rate to make sure it doesn’t increase too quickly.
There are many different classes of antiarrhythmic drugs. The most common of these is atrial fibrillation. There are several different types of antiarrhythmic drugs. Most of these drugs are calcium channel blockers. If you have any type of arrhythmia, you will need a prescription for the drug that will best control your condition. The dosage and frequency of these antiarrhythmic drugs will depend on your age and severity of the disease.
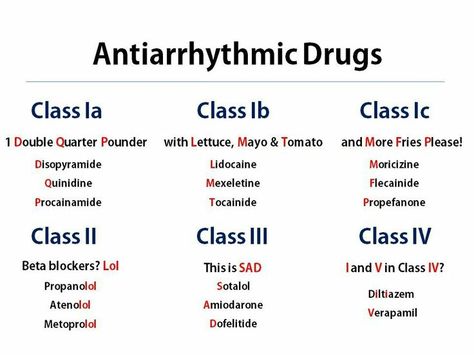
A beta blocker is a type of medication against arrhythmia. It works by inhibiting the actions of certain cells in the heart. This slows down your heart rate. Other arrhythmia medications stop calcium channels in the heart from working. These drugs have side effects and are recommended only in severe cases. These medications are prescribed by a doctor. If these drugs do not help, the site astronomia2009.org.mx may recommend other treatments.
Some of the most common arrhythmias can be treated with different drugs. For instance, beta blockers and calcium channel blockers can prevent atrial fibrillation. They can also be used to control the heart rate. A cardiac specialist will discuss the best treatment option with you. The drugs are prescribed by a physician. In some cases, the medications are not enough to cure the arrhythmia, but they can help you manage symptoms.
The anti-arrhythmia medications can help control heart rhythm. These medicines are commonly used to treat uncomplicated arrhythmias. They are usually administered orally or intravenously. They may be given in oral or intravenous form. The most common medications used to treat arrhythmias are the following: A. The medication must be taken regularly and with a full heart rate. This may increase the risk of side effects.
Another type of arrhythmia medication is a beta-blocker. These medications are designed to inhibit certain cell functions in the heart. They are better for treating uncomplicated abnormal heart rhythms. They are also often prescribed for people with high blood pressure. They are also useful for many other purposes. If you have a heart-rhythm disorder, you may be prescribed a calcium-channel blocker. A beta-blocker can help control heart rate, while a calcium channel blocker will reduce the amount of calcium used by the cell.
In addition to antiarrhythmic drugs, there are other medications available to control arrhythmias. Some of these medicines can cause extracardiac effects and may even worsen your condition. It is important to follow your doctor’s instructions and ask about any side effects. In some cases, you may need to change your diet to lose weight. Taking an antiarrhythmic medication can help control the frequency of irregular heartbeats.
